Advanced water treatment polymer enhances the filtration process.
Advanced water treatment polymer enhances the filtration process.
Blog Article
Explore Exactly How Water Treatment Polymer Features in Efficient Wastewater Treatment Systems
The assimilation of water therapy polymers into wastewater treatment systems represents a substantial advancement in enhancing operational efficiency. These polymers function mainly with mechanisms of coagulation and flocculation, effectively aggregating suspended particles for simpler removal. Their flexibility across differing ecological conditions adds to enhanced sedimentation and decreased sludge volume. Nevertheless, understanding the particular kinds of polymers and their applications can expose deeper insights right into maximizing treatment procedures. What implications do these innovations hold for future wastewater monitoring approaches?
Review of Water Therapy Polymers
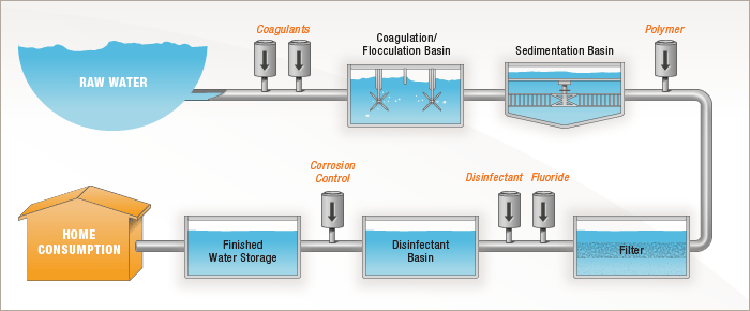
The effectiveness of wastewater monitoring rests on the application of various therapy agents, amongst which water treatment polymers play a pivotal function. These synthetic or all-natural polymers are developed to enhance the effectiveness of physical and chemical processes in wastewater therapy systems. Their primary feature is to help with the gathering of suspended fragments, eventually improving the general quality of cured water.
Water therapy polymers can be classified into a number of groups, consisting of flocculants, coagulants, and dispersants. Coagulants counteract the charges of suspended bits, permitting them to come together and work out a lot more properly.
The application of these polymers not only boosts the removal of pollutants yet also optimizes the operational effectiveness of therapy plants. In addition, the option of suitable water therapy polymers is critical, as their effectiveness can vary based on elements such as water chemistry, temperature, and turbidity levels. Generally, water therapy polymers are important parts in modern wastewater management techniques, adding to cleaner water and sustainable environmental practices.
Mechanisms of Coagulation and Flocculation
Coagulation and flocculation are essential processes in wastewater therapy that symbolize the principles of particle communication and gathering. These systems are critical for getting rid of put on hold solids, colloids, and other impurities from water. Coagulation entails the destabilization of suspended particles, typically attained through the enhancement of coagulants such as steel salts. These coagulants neutralize the electrostatic costs that maintain particles apart, advertising preliminary aggregation.
Complying with coagulation, flocculation occurs, identified by the gentle blending of water to encourage the development of larger accumulations, or flocs. Throughout this stage, polymers play a significant function by bridging in between particles, improving the development of these larger accumulations. The physical and chemical communications during flocculation lead to an increased dimension and thickness of the bits, promoting their subsequent removal via sedimentation or filtration.
The effectiveness of coagulation and flocculation processes is influenced by numerous factors, including pH, temperature level, and the nature of the contaminants present. Understanding these systems permits the optimization of wastewater treatment systems, bring about improved removal effectiveness and total water quality. As a result, the mindful selection and application of coagulants and flocculants are necessary for effective wastewater management.
Kinds Of Water Therapy Polymers
Frequently used in wastewater treatment, water therapy polymers are crucial for enhancing the efficiency of coagulation and flocculation processes. These polymers can be extensively categorized into 3 major kinds: anionic, cationic, and non-ionic.
Anionic polymers, which bring an unfavorable charge, are particularly reliable in dealing with wastewater with favorably charged contaminants. Alternatively, cationic polymers have a favorable fee and are frequently used in applications where adversely billed bits dominate, such as in particular commercial effluents.
Non-ionic polymers, lacking a charge, act as flexible agents that can boost the efficiency of both anionic and cationic polymers. Their main role includes enhancing the viscosity of the wastewater, therefore enhancing the overall retention time of the flocs in the therapy system.
Recognizing the unique qualities of these sorts of water therapy polymers permits the optimization of wastewater treatment procedures, eventually leading to boosted removal performances and enhanced water quality.
Applications in Wastewater Therapy

In municipal wastewater therapy plants, water therapy polymers help decrease the quantity of sludge created throughout the therapy process. water treatment polymer. This reduction not only enhances functional efficiency but likewise lessens disposal expenses linked with sludge monitoring. Additionally, polymers contribute in treating industrial effluents, where they help in the elimination of certain impurities such as hefty steels and organic pollutants, making sure conformity with environmental regulations

Furthermore, water therapy polymers are made use of in the improvement of biofiltration systems, where they enhance microbial activity and general therapy effectiveness. Their role in membrane procedures, such as reverse osmosis, additionally can not be ignored, as they add to membrane fouling control and prolong the life-span of filtration systems. Through these varied applications, water treatment polymers are vital for achieving effective and lasting wastewater administration.
Advantages of Utilizing Polymers
Making use of water therapy polymers in wastewater systems provides numerous advantages that considerably boost treatment performance and general operational efficiency. Firstly, these polymers work as efficient coagulants and flocculants, advertising the aggregation of put on hold solids and facilitating their elimination. This process leads to clearer effluent and lowers the problem on downstream therapy stages.
In addition, polymers improve the dewatering browse around this web-site procedure by improving the sedimentation characteristics of sludge. This leads to lowered volume and weight of waste product, ultimately reducing disposal prices. Moreover, their capability to operate throughout differing pH degrees and temperatures makes sure versatility in different wastewater atmospheres.
Polymers also add to the stabilization of organic procedures by giving nutrients and maintaining have a peek at this website ideal conditions for microbial development - water treatment polymer. This reinforced microbial activity help in the break down of raw material, improving overall therapy performance
Furthermore, the usage of polymers can lead to lowered chemical use, minimizing operational costs and environmental influence. By enhancing the treatment procedure and improving sludge management, water treatment polymers play a vital duty in promoting sustainable wastewater administration methods, aligning with regulatory standards and environmental objectives.
Conclusion
In final thought, water treatment polymers are essential useful reference for boosting the performance of wastewater therapy systems. Their capacity to help with coagulation and flocculation procedures leads to improved sedimentation and reduced sludge quantity, consequently optimizing therapy performance.
Report this page